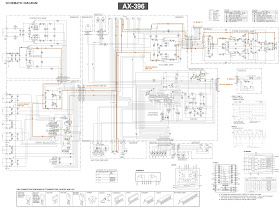
Troubleshooting procedure to Switched Mode Power Supply – using STR G-6653 IC as switching-out device
Fuse F601 (3.15Amps) blows out.
Check
T601 transformer – for its winding short.
If the two of its windings will short each other, the fuse will blow
out.
Check
C602 [0.22/250V] capacitor for short.
Can check it with a multimeter set to measure Kohms range. If shorted, replace it.
The
PTC [R601] short. Check it with
multimeter. If the fuse blows when the
degaussing coil L601 is connected to circuit, and does not when it is
disconnected, the fault is with the PTC itself. Replace it.
Short
circuited [C601A & C601D – 0.0047] ceramic capacitor too can cause the fuse
failure..Check both of them. If found
faulty, replace them. This is a common fault for fuse failure, especially when
the set has hit by lightning.
Shorted
mains rectifier diodes [D601A~D601D], too can cause the fuse failure. Even though any one among them is found
faulty, replace all the four at one time.
It is a best practice in service.
Then
comes the case of mains filter capacitor, C607 [220U/200V]. Short to this capacitor is very rare, might happen some times. So check it too
for any short circuit.
In the case of STR-G6653: The most common
fault happen to it is short circuited Source and Drain of its internal FET [Field Effect Transistor]. It is very easy to check. Check the DC resistance between pin number (1 and 2) of the STR. It will seem to be
short circuited, when we connect the negative prob of the meter to pin-2 and
the positive probe to pin-1; because, there is an internal diode
fabricated inside this IC, which connects the Source and Drain of the internal FET. The cathode of this diode is
connected to pin-1 and the anode to pin-2.
So when we measure, the Dc resistance of (Pin 1 & 2), the DC resistance of this diode might misunderstand as
a FET leak. Reverse the polarity of the
meter probs. There SHOULD NOT be any
short circuit [low ohms measurement]. If
it shows low ohms measurement, the STR is damaged. Have to replace it.
There
are some reasons for this STR to fail.
The first one is a sudden voltage spike at AC input voltage. The other
one is loosely fitted STR to its metal heat sink. If it is loosely fitted, the STR will
overheat and will damage within minutes. Lightning strike.
If
STR is found damaged [leaky], we have to check all the other components on
board, related to STR control circuit.
Make sure that all of them are OK; before replacing the STR with a new
one, other wise the chance of failure to the newly replace STR is about 90%.
Desolder
out the damaged STR from the circuit, and check all the other
components on board, related with it, one by one. If the STR is shorted,
check the two low value resistors [R604 & R603]. Both of them might have opened. These two resistors are connected in parallel
to ground and the pin-2 of the STR through a coil [L602]. Check this coil too for its continuity. Check the high-speed switching diode [D605 IN4148] for short. Replace it with a new one, even it shows no
fault. It is the best. Special care should be given to [C608
0.001u/200v(2Kv)]. If this high voltage
ceramic capacitor is opened or there is any loose solder terminal at any one of
its 2 solder terminals, will cause the STR to burn out.
If this type of fault is there, and we have checked all the other components,
and all of them are found OK; and when we apply AC power to the circuit;
the new STR will blow out within microseconds.
We won’t get no time to measure any of the voltages that cause the damage of
the STR. Keep this in mind always, when
you work with this kind of SMPS. If you
have a capacitance meter. Measure the capacitance of this
capacitor, and make sure it is good, and has not shorted or opened. If this capacitor has a direct short circuit,
inside, the fuse will blow out. See how it is connected. Refer the circuit diagram. One terminal is
connected to main DC rail (+), through [L601] and the primary winding of
[T603] and the other to Ground (-). Now it is clear for the reason the fuse blows.
Check
the transistor [Q601 – 2SC2482] and make sure that it is good. Check the 15V Zener diode [ZD602] for any
leak. Desolder this diode out from
circuit, and check it by multimeter (analogue type) set to KOhms range. There shouldn’t be any reverse reading to this
diode.
If
all these checks are over, you can insert the new STR in place, screw it hard to
its metal heat-sink (apply heat-sink compound, is highly recommended). Never power ON the circuit now. Disconnect the (B+) supply rail [the DC output of the SMPS] from the rest of the circuit.
Connect a 100W filament type bulb [do not use CFL or such type]. Re-check all the work done so far and make
sure all are OK. Check all the solder
terminals at the SMPS section circuit for any dry solder. Re-solder any suspected,
by applying a little more solder; without making any solder bridge short in
between adjacent terminals.
Power
ON the circuit. If all are OK; the
connected bulb will glow [at first it will show a bright light; and within 3 seconds or so, it will go dim]
Now measure the voltage across [C616].
It should snow around 110VDC. Keep the
circuit connected to AC, and watch the luminescence of the bulb. There shouldn’t be any flicker or flicker effect. Keep
connected; and check its line to load regulation at about 20 minutes. After that, you can connect the rest of
the circuit, after removing the bulb.
The SMPS refuses to start, even though all the components on
board are OK.
Sometimes,
the power supply regulator won’t start, as soon as the main power switch is ON. Sometimes, it will start
after several attempts of power On/Off.
This is the fault to the start supply voltage to the SMPS. Make sure that the contact of the main ON/Off switch is Ok.
Here
with this circuit, you can note that there is a 3W resistor connected to the
pin-4 of the STR, in series with main AC line.
The pin-4 is connected to the emitter of [Q601] too. This is the start and retain voltage section. What happens when we switch ON the set
for the first time is, the pin-4 of the STR will get a low voltage through R607 from AC mains;
and its control block inside will start up to work. The STR will start to work, and the
SMPS transformer too. After the SMPS
transformer start to work, it will generate a voltage, which is converted to DC
by [D610 BA158], and that voltage is further regulated by Q601, and then
supplied back to the pin-4 of the STR. This voltage will take over the STR’s control block to work,
till we switch OFF the set. When we
switch ON the set again, the same functions as described above will
happen. So, when this fault is noted [delayed start up], make sure that the [R607 – 39K3W] and its solder
terminals too are OK, and R607 is not open. Check the (R605 & R608 (2M2)) resistors too for open circuit.